what is organic farming class 8
Organic farming is a method of growing crops and raising livestock without the use of synthetic chemicals such as fertilizers, pesticides, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Organic farming is based on the principles of maintaining soil health and fertility, promoting biodiversity, and avoiding the use of harmful chemicals that can negatively impact the environment and human health.
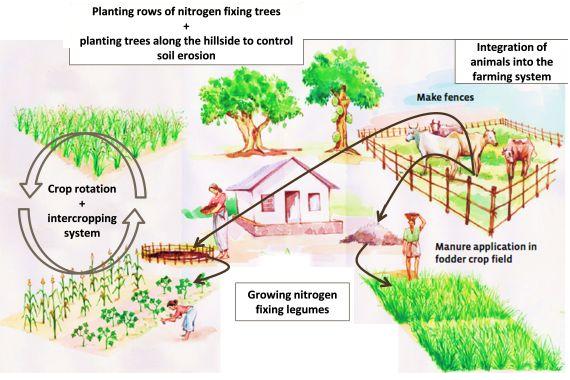
In class 8, students may learn about the basic principles of organic farming, such as the use of natural inputs such as compost, manure, and cover crops to maintain soil fertility, crop rotation to reduce pests and diseases, and the importance of preserving biodiversity through the use of traditional seeds and farming practices.
Students may also learn about the benefits of organic farming, such as improved soil health, reduced water consumption, and increased biodiversity. Organic farming can also help to improve food security, particularly for small-scale farmers, by increasing crop yields and reducing dependence on costly inputs such as synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
Additionally, class 8 students may learn about the challenges of organic farming, such as the higher labor costs associated with organic farming, the difficulty in finding markets for organic produce, and the need for more training and technical support for farmers who are interested in transitioning to organic farming.
Overall, organic farming is a sustainable approach to agriculture that can help to promote environmental, social, and economic benefits. By learning about organic farming in class 8, students can gain a deeper understanding of the importance of sustainable agriculture and the role that they can play in promoting a healthier, more sustainable food system.
what is organic farming
class 9
Organic farming is a method of farming that does not use synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in the production of crops or livestock. Instead, organic farming relies on natural inputs such as compost, manure, and cover crops to maintain soil fertility and promote plant growth.
In class 9, students may learn about the basic principles of organic farming, such as the use of natural inputs to maintain soil fertility, crop rotation to reduce pests and diseases, and the importance of preserving biodiversity through the use of traditional seeds and farming practices.
Students may also learn about the benefits of organic farming, such as improved soil health, reduced water consumption, and increased biodiversity. Organic farming can also help to improve food security, particularly for small-scale farmers, by increasing crop yields and reducing dependence on costly inputs such as synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
Additionally, class 9 students may learn about the challenges of organic farming, such as the higher labor costs associated with organic farming, the difficulty in finding markets for organic produce, and the need for more training and technical support for farmers who are interested in transitioning to organic farming.
Overall, organic farming is a sustainable approach to agriculture that can help to promote environmental, social, and economic benefits. By learning about organic farming in class 9, students can gain a deeper understanding of the importance of sustainable agriculture and the role that they can play in promoting a healthier, more sustainable food system.
what is organic farming class 10
In class 10, students may learn more advanced concepts related to organic farming, including the principles of soil health, crop rotation, and natural pest management. They may also learn about the different types of organic farming systems, such as agroforestry, intercropping, and conservation agriculture.
Class 10 students may also learn about the importance of biodiversity in organic farming and the role that traditional farming practices can play in preserving local ecosystems. They may study the effects of climate change on agriculture and the ways in which organic farming can help to mitigate these effects.
In addition, class 10 students may explore the social and economic impacts of organic farming, including the potential for organic farming to promote food security, improve soil health, and support rural development. They may also study the challenges faced by organic farmers, including the need for specialized knowledge and training, access to markets, and adequate infrastructure and support systems.
Overall, the study of organic farming in class 10 can provide students with a deeper understanding of the importance of sustainable agriculture and the ways in which organic farming can help to promote environmental, social, and economic sustainability. By studying organic farming, students can develop the knowledge and skills needed to promote a more sustainable food system and contribute to a healthier, more resilient planet.
what is organic farming class 11
In class 11, students may study organic farming in greater depth, focusing on the scientific principles behind organic farming practices and the ways in which organic farming can help to promote sustainable agriculture.
Class 11 students may learn about the role of soil biology in organic farming, including the importance of beneficial soil organisms such as mycorrhizal fungi and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. They may also study the effects of different soil management practices, such as cover cropping and composting, on soil health and plant growth.
In addition, class 11 students may learn about the principles of natural pest management, including the use of beneficial insects, crop rotation, and companion planting to reduce pest populations without the use of synthetic pesticides. They may also study the use of organic fertilizers and other natural inputs to promote plant growth and improve soil health.
Class 11 students may also study the policy and regulatory landscape surrounding organic farming, including the certification process and the ways in which organic farming is promoted and supported by government programs and initiatives.
Overall, the study of organic farming in class 11 can provide students with a more advanced understanding of the scientific principles and practical applications of sustainable agriculture. By studying organic farming, students can develop the knowledge and skills needed to promote a more sustainable food system and contribute to a healthier, more resilient planet.
what is organic farming class 12
In class 12, students may study organic farming in greater detail, focusing on advanced topics such as organic certification, agroecology, and the economics of organic farming.
Class 12 students may learn about the various organic farming certification programs and the requirements for organic certification. They may also study the role of standards and regulations in organic farming and the ways in which organic certification helps to promote consumer confidence and ensure the integrity of organic products.
In addition, class 12 students may explore the principles of agroecology, which emphasizes the importance of ecological relationships in agriculture and seeks to create resilient, self-regulating farming systems. They may study the ways in which agroecology can help to promote soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem services, and how it differs from traditional approaches to farming.
Class 12 students may also study the economics of organic farming, including the costs and benefits of transitioning to organic farming, the potential for organic farming to support rural development and improve livelihoods, and the challenges faced by organic farmers in accessing markets and obtaining fair prices for their products.
Overall, the study of organic farming in class 12 can provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the scientific, economic, and policy aspects of sustainable agriculture. By studying organic farming, students can develop the knowledge and skills needed to promote a more sustainable food system and contribute to a healthier, more resilient planet.







0 Comments